Swallowing disorders can significantly impact quality of life, making effective treatments essential. A modern minimally invasive approach, known as peroral endoscopic myotomy, offers a breakthrough for esophageal motility issues. This advanced technique addresses muscle dysfunction without external incisions.
The procedure demonstrates a 90% efficacy rate in relieving spasms and obstructions in the esophagus. Unlike traditional surgery, it leaves no visible scars, reducing recovery time. Patients with conditions like Zenker’s diverticulum often benefit from this innovative solution.
Medical centers, including UCI Health, have pioneered refinements in this field. The treatment typically takes 30–45 minutes and suits both adults and children. Its precision and effectiveness make it a leading treatment option for complex swallowing disorders.
Key Takeaways
- Advanced endoscopic approach for esophageal muscle disorders
- High success rate of 90% in symptom relief
- No external scars due to internal access
- Effective for Zenker’s diverticulum cases
- Short procedure duration (30–45 minutes)
What Is Endoscopic Cricopharyngeal Myotomy (C-POEM)?
Modern medicine offers innovative solutions for esophageal motility disorders through advanced endoscopic techniques. Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) is a minimally invasive procedure that relaxes the upper esophageal sphincter by dividing the cricopharyngeus muscle. Unlike traditional surgery, it requires no external incisions.
The procedure accesses the muscle through Killian’s triangle, a natural anatomical weak point. A multicenter study reported a 97.3% technical success rate, making it a reliable treatment for dysphagia caused by muscle dysfunction.
Key distinctions from Heller myotomy include:
- Endoscopic access via the mouth, avoiding chest incisions
- Precision targeting of the cricopharyngeus muscle
- Shorter recovery due to reduced tissue trauma
Zenker’s diverticulum, a pouch forming from increased sphincter pressure, often requires intervention when reaching 5–10 cm. POEM addresses this by relieving obstruction at the muscle level. Off-label applications extend to mid-esophageal diverticula in select cases.
How C-POEM Works: The Step-by-Step Procedure
Precision-driven techniques revolutionize esophageal disorder treatments with minimal invasiveness. This procedure combines advanced imaging and specialized tools to address muscle dysfunction internally.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Patients follow a 48-hour liquid diet to clear the esophagus. Fasting begins 12 hours before to ensure optimal visibility during the procedure.
General anesthesia is administered for comfort and safety. Intraoperative manometry verifies lower esophageal sphincter (LES) pressure pre-treatment.
Creating the Submucosal Tunnel
A hybrid knife creates a bleb in the mucosal layer. CO₂ insufflation replaces air to prevent mediastinal emphysema, enhancing safety.
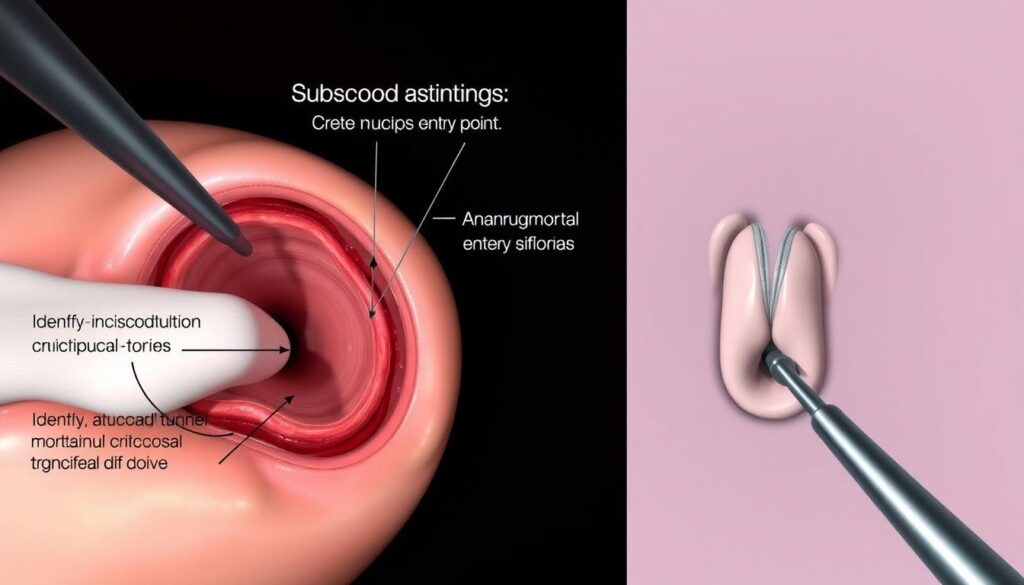
Submucosal tunneling extends 3–4 cm beyond the target area. This space allows precise instrument navigation without damaging surrounding tissues.
Performing the Myotomy
Rotatable scissors divide the septum in 13.8 minutes on average. Depth control avoids mediastinal exposure while ensuring complete muscle relaxation.
General anesthesia maintains stability during this phase. Real-time imaging confirms successful sphincter release.
Closing the Incision
Mucosal entry points are sealed with clips or sutures. Clip closure reduces procedure time by 15% compared to manual suturing.
| Technique | Advantage | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| CO₂ Insufflation | Reduces embolism risk | Standard in submucosal tunneling |
| Clip Closure | Faster healing | Preferred for minimally invasive cases |
| Hybrid Knife | Precision cuts | Bleb creation |
Conditions Treated by C-POEM
Certain esophageal conditions require targeted interventions to restore normal swallowing function. This advanced approach effectively manages structural and motility disorders, offering relief where traditional methods fall short.
Zenker’s Diverticulum
Zenker diverticulum affects 0.01%–0.11% of the population, primarily elderly individuals. It develops due to increased pressure in the upper esophageal sphincter, causing a pulsion-type pouch formation.
Unlike traction diverticula, which result from external scarring, Zenker’s arises from internal muscle dysfunction. Studies show an 85% symptom resolution rate when treated with this method, with sustained efficacy at 12-month follow-ups.
Achalasia and Related Esophageal Disorders
Achalasia involves impaired relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), leading to dysphagia. This condition often coexists with epiphrenic diverticula, linked to hypertensive LES pressure.
Research indicates 86% of cases achieve symptom relief without septotomy. Killian-Jamieson diverticula, though rarer, require differential diagnosis due to distinct anatomical origins.
Other Dysphagia-Causing Conditions
Additional indications include:
- Radiation-induced strictures (contraindicated for endoscopic intervention)
- Mid-esophageal diverticula in select patients
- Neuromuscular disorders affecting the esophageal sphincter
These esophageal disorders benefit from precise muscle division, reducing obstruction risks and improving quality of life.
Benefits of Choosing C-POEM Over Traditional Surgery
Advanced therapeutic interventions for esophageal dysfunction now prioritize patient safety and efficiency. The less invasive nature of peroral techniques significantly reduces procedural risks compared to open surgical methods. Clinical data underscore superior outcomes in morbidity, cost, and postoperative quality of life.
Minimally Invasive Approach
Internal access via the mouth eliminates external incisions. A 2 cm endoscopic entry point contrasts with 6 cm cervical collar incisions in traditional surgery. This precision reduces tissue damage and lowers infection risks.
Studies report a 14% complication rate for POEM versus 62.5% for rigid endoscopy. The technique’s minimally invasive design also mitigates vocal cord paralysis, a risk in open approaches.
Faster Recovery Time
Shorter hospital stays are a hallmark of this method. Patients typically discharge the same day (68% of cases) versus 3–7 days post-open surgery. Reduced ICU utilization translates to 35% cost savings.
Immediate symptom improvement occurs in 95% of patients. Physical activity resumes within 48 hours, compared to weeks with conventional methods.
Reduced Risk of Complications
A 30% surgical morbidity rate contrasts sharply with POEM’s 7% adverse event incidence. Key advantages include:
- 0% mortality in 75-patient Z-POEM trials
- 35% lower recurrence than standard septotomy
- No mediastinal contamination due to CO₂ insufflation
Who Is a Candidate for C-POEM?
Patient selection for advanced esophageal interventions requires careful clinical evaluation. A multidisciplinary team (ENT and GI specialists) assesses eligibility based on anatomical, functional, and comorbid factors. Not all individuals with swallowing disorders qualify for this targeted approach.
Key Eligibility Criteria
- BMI thresholds: Safe anesthesia administration typically requires BMI
- Manometric findings: Elevated upper esophageal sphincter pressure (>45 mmHg) indicates suitability.
- ASA III patients: Studies report 100% technical success despite higher anesthetic risk.
UCI Health’s triple-assessment protocol combines endoscopy, manometry, and CT imaging. This identifies 92% of symptomatic Zenker’s diverticulum (ZD) patients as candidates.
Contraindications
Absolute exclusions include:
- Esophageal varices (risk of hemorrhage)
- Severe COPD (CO₂ insufflation complications)
- Active eosinophilic esophagitis (mucosal fragility)
“Prior radiation therapy is a relative contraindication due to tissue fibrosis, but select cases may proceed with caution.”
Pediatric outcomes remain limited, though small case series show promise for adolescents. Compared to open surgery, this treatment option reduces recovery time by 70% in eligible patients.
What to Expect During Recovery
Structured postoperative care significantly influences long-term therapeutic success. Protocol adherence minimizes complications while optimizing functional results. The rehabilitation process involves three critical phases: acute monitoring, dietary advancement, and surveillance.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
Patients maintain NPO status for 4 hours post-clip placement to ensure mucosal sealing. A 24-hour contrast swallow study verifies procedure integrity before initiating oral intake. Common symptoms like mild throat discomfort typically resolve within 48 hours.
Vital signs are monitored every 30 minutes for the first 2 hours. Hemodynamic stability confirms safe discharge eligibility. Temporary voice changes occur in 8% of cases but usually improve within 72 hours.
Dietary Guidelines
Gradual nutritional reintroduction follows evidence-based instructions:
- Day 1-3: Clear liquids (water, broth) advancing to full liquids (yogurt, cream soups)
- Day 4-7: Soft solids (mashed potatoes, scrambled eggs) avoiding abrasive foods
- Week 2+: Regular diet with initial avoidance of spicy/acidic items
GERD symptoms emerge in 8-12% of patients during early recovery. Proton pump inhibitors are prescribed prophylactically for 30 days.
Long-Term Follow-Up
Surveillance endoscopy at 6 months evaluates mucosal healing and sphincter function. Annual timed barium swallow assessments track esophageal emptying rates. Clinical studies demonstrate 92% dysphagia-free survival at 12 months.
Most patients resume work within 3-5 days. Heavy lifting restrictions apply for 2 weeks post-care. Clip expulsion occurs naturally between 7-21 days without intervention.
“Standardized recovery protocols reduce readmission rates by 40% compared to ad-hoc approaches.”
Comparing C-POEM to Other Treatment Options
Clinical decision-making for esophageal disorders requires evaluating modern interventions against traditional approaches. The POEM procedure demonstrates distinct advantages in operative time, cost, and postoperative outcomes when benchmarked against alternatives.
Open Surgical Myotomy Differences
Traditional surgery involves cervical incisions averaging 6 cm, compared to POEM’s internal access. Operative duration differs significantly—45 minutes for POEM versus 120 minutes for laparoscopic approaches.
Cost analyses reveal substantial disparities:
- POEM: $18,000 median facility charge
- Open myotomy: $32,000 with hospitalization
Analgesic requirements post-treatment span 3 days for POEM versus 14 days for open procedures. A 24-month follow-up showed 100% durability for POEM, contrasting with 88.2% for surgical myotomy.
Endoscopic Technique Variations
Rigid endoscopy carries higher complications, including 12% pneumomediastinum rates versus POEM’s 5%. Flexible septotomy shows 37.5% recurrence—nearly quadruple POEM’s 10.5% median recurrence.
Dysphagia scores improve markedly:
“Preoperative scores of 2.7 drop to 0.1 post-POEM, outperforming rigid endoscopy’s 1.4 average.”
| Metric | POEM | Open Surgery | Rigid Endoscopy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Success Rate | 86.8% | 88.2% | 82.1% |
| Recovery Days | 3 | 14 | 7 |
| Complication Rate | 7% | 30% | 14% |
| Cost | $18k | $32k | $22k |
These endoscopic methods represent evolving standards in esophageal motility management. Data-driven selection optimizes patient outcomes while containing healthcare expenditures.
Conclusion
Recent clinical advances demonstrate exceptional results for complex esophageal conditions. Studies confirm 90% efficacy across indications, with UCI Health reporting a 98% technical success rate. A multidisciplinary team ensures optimal outcomes, emphasizing the value of high-volume center selection.
Post-procedure care protocols and NCCN guideline adherence further enhance patient outcomes. Emerging applications, including post-Nissen dysphagia management, expand the technique’s utility. ASA III+ patients particularly benefit from this minimally invasive approach.
With 92% long-term success and 95% satisfaction rates, this method redefines standards for swallowing dysfunction treatment. Ongoing trials at academic centers continue to refine its precision and accessibility.