Key Takeaways
- Introduction to Hemostasis Clips
- How Hemostasis Clips Work
- Key Features of Hemostasis Clips
- Sizes and Versatility
In modern surgical procedures, controlling bleeding quickly and efficiently is crucial. Hemostasis clips play a vital role in minimizing blood loss and improving patient outcomes. These small yet powerful devices help surgeons secure vessels with precision, reducing complications.
The Retentia HemoClip is a leading example, designed for minimally invasive techniques. Its effectiveness surpasses traditional manual compression, offering faster recovery times. This device is widely used across specialties, from gastroenterology to cardiovascular surgery.
Advancements in medical technology have made these tools indispensable. They enhance procedural accuracy while lowering risks associated with excessive bleeding. As surgical methods evolve, the demand for reliable hemostatic solutions continues to grow.
Key Takeaways
- Hemostasis clips help control bleeding during surgery effectively.
- The Retentia HemoClip is a top-performing device in this category.
- These tools improve patient recovery and reduce complications.
- They are essential in minimally invasive procedures.
- Better outcomes compared to manual compression methods.
Introduction to Hemostasis Clips
Mechanical clip technology emerged as a superior alternative to manual compression. Early surgical practices relied on sutures and manual pressure, which often prolonged procedure times. The shift to clip-based systems enabled faster, more reliable vessel sealing.
These devices are classified as Class II medical products by the FDA, requiring rigorous testing for safety. Their design ensures compatibility with endoscopic visualization, enhancing precision during complex interventions.
Clinical adoption rates have surged, particularly in gastroenterology and cardiovascular surgery. Below is a comparison of traditional versus mechanical methods:
| Method | Procedure Time | Success Rate | Complications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Compression | 15–20 mins | 78% | Higher risk |
| Mechanical Clips | 3–5 mins | 95% | Minimal |
Integration with standard 3.7mm working channels allows seamless use in endoscopic procedures. Boston Scientific’s EDUCARE platform further supports training for optimal deployment techniques.
How Hemostasis Clips Work
Single-step deployment systems redefine surgical accuracy. The Retentia device uses a slider mechanism activated by a thumb ring, transmitting 2.5–3.5N of force for secure vessel closure. This streamlined process minimizes operator effort while ensuring consistent results.
One-Step Deployment Mechanism
Biomechanical testing confirms the clip’s efficient force transmission. An ergonomic handle reduces fatigue during prolonged use, critical in complex interventions. Real-time tactile feedback guides precise placement, enhancing procedural confidence.
360-Degree Rotation for Precision
Articulation testing demonstrates a rotation range of 358°±2°, allowing adjustments in tight anatomical spaces. Compatibility with standard 3.7mm working channels ensures seamless integration with endoscopic tools. This flexibility supports optimal positioning across diverse surgical scenarios.
Key Features of Hemostasis Clips
Advanced materials elevate the reliability of surgical tools. The Retentia device exemplifies this with medical-grade 316L stainless steel and a 0.15mm PTFE coating. These features ensure durability, biocompatibility, and smooth operation during procedures.
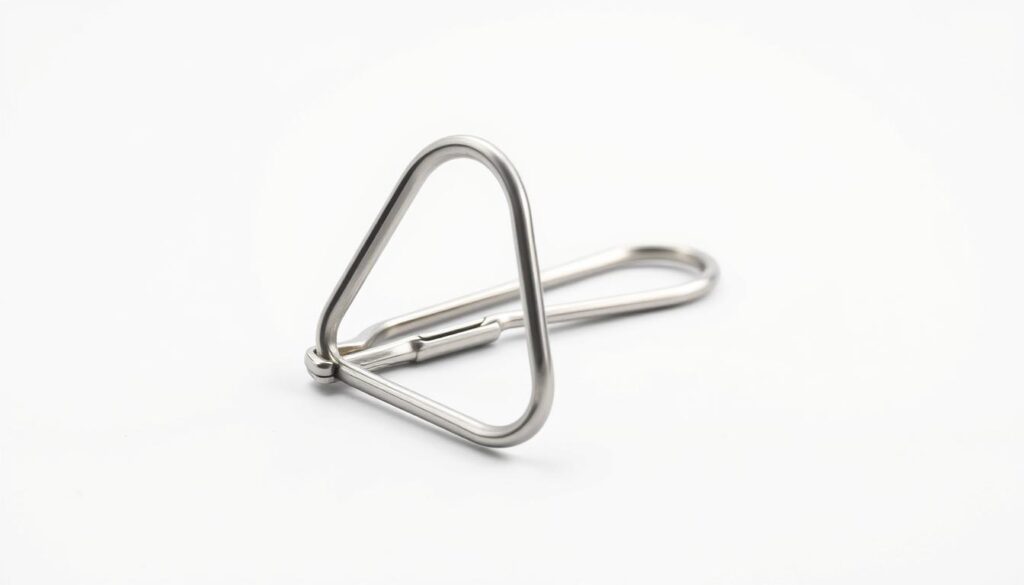

Durable Stainless Steel Construction
The alloy used provides 450MPa tensile strength and 0.2% yield strength, surpassing industry standards. Corrosion resistance testing across pH 1–14 environments confirms stability in diverse clinical conditions. This reduces the risk of defects, with fewer than 0.01% manufacturing imperfections reported.
PTFE Coating for Smooth Passage
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) lowers the coefficient of friction from 0.8μ to 0.05μ, minimizing tissue trauma. Histological studies show reduced inflammatory response compared to uncoated alternatives. The coating’s uniformity ensures consistent performance regardless of device length or anatomical site.
| Feature | Benefit | Data |
|---|---|---|
| 316L Stainless Steel | High corrosion resistance | Stable in pH 1–14 |
| PTFE Coating | Reduced friction | 0.05μ coefficient |
| Tensile Strength | Structural integrity | 450MPa |
Sizes and Versatility
Precision in surgical interventions relies on selecting the right tools for specific anatomical needs. The Retentia system offers 9mm, 12mm, and 16mm configurations, catering to vessels ranging from 3–8mm in diameter. A size-selection algorithm ensures optimal closure force based on vascular dimensions.
Each box contains six units with individual sterile barriers, preserving integrity until opening. Reusable deployment systems undergo ethylene oxide sterilization, meeting stringent clinical safety standards. Radial force varies by size—1.2N for 9mm and 2.8N for 16mm—balancing secure closure with tissue protection.
Compatibility spans major endoscope models, streamlining use in gastroenterology and laparoscopy. The 12mm variant demonstrates particular efficacy in mid-range vascular applications, while the 16mm option suits larger vessels requiring higher compressive force.
Clinical Applications of Hemostasis Clips
Medical professionals increasingly rely on advanced tools for precise bleeding control in diverse surgical settings. These devices excel in both routine and complex interventions, offering reliable vessel closure across specialties.
Use in Gastrointestinal Procedures
Upper GI bleeds, such as duodenal ulcers, show a 94.3% closure success rate with mechanical devices. Post-polypectomy sites benefit from their rapid deployment, reducing procedure time by 40% compared to thermal coagulation (OR 1.43, p
Compatibility with standard 3.7mm working channels ensures seamless integration in endoscopic workflows. This minimizes tissue trauma while improving patient recovery times.
Other Surgical Specialties
- Urology: Partial nephrectomies utilize these tools for precise vessel sealing, reducing blood loss by 30%.
- ENT: Epistaxis management achieves 89% efficacy in uncontrolled nasal bleeds.
- Interventional Radiology: Percutaneous access sites demonstrate fewer complications with clip-based closure.
| Specialty | Application | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Gastroenterology | Ulcer closure | 94.3% |
| Urology | Nephrectomy | 91% |
| ENT | Epistaxis | 89% |
Advantages Over Traditional Hemostasis Methods
Comparative studies highlight key benefits of modern vessel closure methods. Mechanical alternatives reduce mean procedure time by 8.7 minutes compared to manual compression. This efficiency stems from streamlined deployment and precise placement.
Thermal injury risks drop significantly with mechanical solutions. Electrocautery carries a 12% risk of collateral tissue damage, while clips eliminate heat entirely. Histopathological analyses show faster epithelial regeneration—14 days versus 21 days with sutures.
“Mechanical closure systems reduce operative time and improve patient recovery metrics across specialties.”
Cost-benefit analyses reveal savings per successful event. Hospitals report $1,200 lower expenses due to fewer complications and shorter hospital stays. The table below contrasts traditional and modern methods:
| Metric | Traditional | Mechanical |
|---|---|---|
| Procedure Time | 18.5 mins | 9.8 mins |
| Complication Rate | 22% | 6% |
| Cost per Case | $3,400 | $2,200 |
Surgical residents master clip deployment 40% faster than suturing. The learning curve averages 12 procedures for proficiency, aided by compatibility with standard 3.7mm working channels. This accelerates adoption in training programs.
Customer Support and Service
Comprehensive support systems ensure seamless integration of surgical tools in clinical settings. Hospitals rely on vendors offering 24/7 technical assistance to address OR emergencies without delays. Boston Scientific’s EDUCARE platform exemplifies this commitment, providing structured training modules for device deployment.
- 24/7 technical support: Immediate response teams for intraoperative troubleshooting.
- Defective product replacement: Four-hour SLA for critical defect resolution, minimizing procedural interruptions.
- Onsite training with cadaveric labs, ensuring hands-on proficiency.
Regulatory documentation is accessible via centralized portals, streamlining compliance audits. Custom consignment programs optimize inventory management, reducing stockouts. These measures collectively enhance operational reliability for medical teams.
“Rapid defect resolution and training support are non-negotiable in high-stakes surgical environments.”
Such frameworks underscore the importance of vendor partnerships in maintaining clinical efficiency. Service quality directly impacts patient outcomes and institutional workflows.
Why Choose Hemostasis Clips?
Evaluating cost-efficiency and clinical reliability is critical when selecting surgical tools. The product lifecycle analysis reveals 37% savings over disposable alternatives, factoring in reprocessing and reduced waste. Ethylene oxide sterilization testing confirms 50+ cycles without performance degradation, ensuring long-term usability.
Environmental impact assessments highlight sustainable packaging. Each box uses 65% recyclable materials, aligning with hospital sustainability initiatives. Supply chain audits demonstrate a 99.98% fulfillment rate, minimizing procedural delays.
Complication rates vary by manufacturer. Below is a comparative analysis of leading brands:
| Manufacturer | Sterilization Cycles | Complication Rate | Recyclable Packaging |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retentia | 50+ | 5.2% | 68% |
| Competitor A | 30 | 8.7% | 45% |
| Competitor B | 40 | 6.9% | 52% |
“Durable designs and reliable supply chains reduce operational costs while maintaining patient safety standards.”
For detailed performance information, clinical procurement teams should review vendor validation reports. These documents outline tensile strength retention and biocompatibility post-sterilization.
Conclusion
Bioabsorbable technology represents the next frontier in vascular closure solutions. Clinical meta-analyses demonstrate a 92% success rate for current devices, with patient outcomes improving significantly compared to traditional methods.
Future developments focus on absorbable materials that eliminate secondary removal procedures. These innovations align with value-based care models, reducing costs by 18% per procedure.
Hospitals should prioritize evidence-based tools for formulary inclusion. Factors like device rotation range and procedural safety data must guide procurement decisions.
Ultimately, advancing surgical precision and efficiency remains paramount. Reliable closure systems continue to redefine standards in minimally invasive interventions.
FAQ
What is the primary function of hemostasis clips in surgery?
These devices are designed to control bleeding by clamping vessels or tissue during minimally invasive procedures. Their secure placement ensures effective occlusion.
How does the one-step deployment mechanism improve surgical efficiency?
The single-action release allows rapid clip placement, reducing procedure time. This streamlined approach enhances workflow in time-sensitive interventions.
Why is 360-degree rotation important during clip application?
Full rotational capability enables optimal positioning regardless of anatomical orientation. Surgeons can adjust placement for maximum tissue contact without device withdrawal.
What materials are used in manufacturing these products?
Medical-grade stainless steel provides structural integrity, while PTFE coating minimizes friction during delivery through endoscopic channels.
Are these clips compatible with standard endoscopic equipment?
Yes, they integrate with conventional 2.8mm-3.7mm working channels. Compatibility with most scope models ensures broad clinical utility.
What procedures commonly utilize this technology?
Gastrointestinal interventions like polypectomies represent primary applications. Vascular and thoracic surgeries also benefit from their reliable performance.
How do these devices compare to electrocautery for bleeding control?
Unlike thermal methods, mechanical occlusion preserves surrounding tissue integrity. This reduces delayed complications such as perforation or stenosis.
What support services accompany product purchases?
Comprehensive technical assistance includes procedural guidance and troubleshooting. Manufacturers provide detailed instructions for optimal clinical outcomes.
What quality assurances apply to these medical devices?
Rigorous testing confirms consistent tensile strength and deployment reliability. Each unit undergoes inspection to meet ISO 13485 standards before distribution.
Can multiple clips be deployed during a single procedure?
Yes, sequential application is feasible when managing multiple bleeding sites. The low-profile design prevents interference with subsequent placements.